Tau-aggregation and neuroinflammation-IN-1
CAS No. 2175953-98-5
Tau-aggregation and neuroinflammation-IN-1( —— )
Catalog No. M35680 CAS No. 2175953-98-5
Tau-aggregation and neuroinflammation-IN-1 is a potent inhibitor of tau protein aggregates, showing significant inhibitory activity against AcPHF6 and full-length tau protein aggregates.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 5MG | 37 | Get Quote |


|
| 10MG | 61 | Get Quote |


|
| 25MG | 112 | Get Quote |


|
| 50MG | 181 | Get Quote |


|
| 100MG | 264 | Get Quote |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameTau-aggregation and neuroinflammation-IN-1
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionTau-aggregation and neuroinflammation-IN-1 is a potent inhibitor of tau protein aggregates, showing significant inhibitory activity against AcPHF6 and full-length tau protein aggregates.
-
DescriptionTau-aggregation and neuroinflammation-IN-1 is a potent tau-aggregation and neuroinflammation inhibitor. Tau-aggregation and neuroinflammation-IN-1 exhibits remarkable inhibitory activities against AcPHF6 and full-length tau aggregation. Tau-aggregation and neuroinflammation-IN-1 has a low cytotoxicity and reduced NO release in LPS-stimulated BV2 cells. Tau-aggregation and neuroinflammation-IN-1 can reverse okadaic acid-induced memory impairment in rats.
-
In VitroTau-aggregation and neuroinflammation-IN-1 (compound 30) (0-40 μM) reduces the survival of SH-SY5Y cells at 30 μM, and exerts no significant hepatotoxicity in LO2 cells at high concentrations, also exerts no effect on BV2 cell viability at 20 μM.Tau-aggregation and neuroinflammation-IN-1 (2.5, 5 and 10 μM; 24 hours) retains the anti-inflammatory activity of sodium usnate and inhibits NO release rate by 41% in LPS-stimulated BV2 cells at 10 μM.Cell Cytotoxicity Assay Cell Line:SH-SY5Y, LO2 and BV-2 cells Concentration:0, 10, 20, 30 and 40 μM Incubation Time:24 hours Result:Reduced the survival of SH-SY5Y cells at 30 μM, and exerted no significant hepatotoxicity in LO2 cells even at high concentrations (up to 40 μM), also exerted no effect on BV2 cell viability at 20 μM.
-
In VivoTau-aggregation and neuroinflammation-IN-1 (5 and 10 mg/kg; for 14 days) leads to a substantial improvement of the conventional reference spatial memory and cognitive abilities of OA-induced rats.Animal Model:Male SD rats (250-270 g; OA was microinjected into the right dorsal hippocampus)Dosage:5 and 10 mg/kg Administration:IP; for 7 days, and after OA-injection continued IP for 7 days Result:Led to a substantial improvement of the conventional reference spatial memory and cognitive abilities of rats.
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorMicrotubule Associated | NO Synthase
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number2175953-98-5
-
Formula Weight460.44
-
Molecular FormulaC25H20N2O7
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityIn Vitro:?DMSO : 125 mg/mL (271.48 mM; Ultrasonic )
-
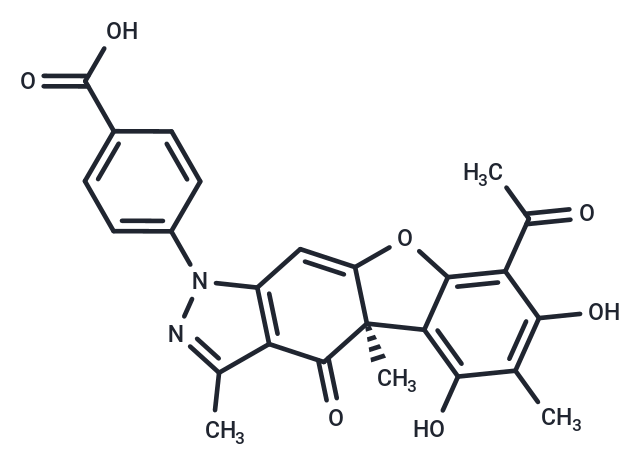
SMILESC[C@@]12C=3C(OC1=CC4=C(C2=O)C(C)=NN4C5=CC=C(C(O)=O)C=C5)=C(C(C)=O)C(O)=C(C)C3O
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1. Shi CJ, Peng W, Zhao JH, et al. Usnic acid derivatives as tau-aggregation and neuroinflammation inhibitors. Eur J Med Chem. 2020;187:111961.?
molnova catalog



related products
-
Juncusol
Juncusol shows anxiolytic and sedative activities, it shows anxiolytic activity at dosages of 10 mg/kg; it can induce caspase-3-mediated cytotoxicity in HT22 cells. Juncusol has anti-microbial activity, it shows significant activity against MRSA strains.
-
Nesfatin-1 (human)
Nesfatin-1 (human)
-
Coumarin-3-carboxyli...
The combination of Valproic acid with coumarin-3-carboxylic acid suppresses the proliferation and migration of lung cancer cells via EGFR/VEGFR2/c-Met-Akt-NF-κB signaling pathways.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


